Protect an attribute
To ensure the stability, maintainability, and reusability of your content, you can mark an attribute as Protected. If you mark an attribute as protected, it prevents authors from altering the attribute in the Oxygen editor. By default, only administrators can alter a protected attribute in the Oxygen editor. If you also want to give this ability a specific user or role, you must give them special permissions.
![]() You must be an Administrator to complete these steps.
You must be an Administrator to complete these steps.
 Tips and tricks
Tips and tricks
- For more examples of using protected attributes, read Why would I want to protect an attribute?
- By default, when creating an attribute, the Protected option is not selected.
- You can select Protected in conjunction with any other property such as Profiled, Identifier, or Language.

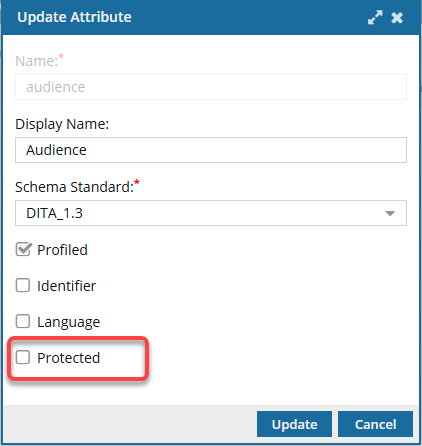
If an attribute has the Protected property :
In the Oxygen editor, to delete or update protected attributes, users must have one of the following permissions:
Permissions to the can_modify_protected_attributes property
- Administrator
This protection is enforced in the Oxygen editor in the following places:
Author mode
Edit XML Source mode
- Reviews
- Resolving reviews

 Before you begin
Before you begin
You cannot protect a single instance of an attribute.
- If you select the Protected option for an attribute, such as href, all uses of that href attribute are locked.
- Users cannot update or delete any use of the Protected attribute in the Oxygen editor unless they are an administrator or have special permissions.
- Users can add the Protected attribute to a document, but cannot change its value.
- For example, if you protect the scalefit attribute that has a default value of Yes, any user can add this attribute to an image element, and it will have a value of Yes.
- Users cannot change the scalefit's value to anything else without permissions.

 These steps explain how to update an existing attribute to protect it in the Oxygen editor.
These steps explain how to update an existing attribute to protect it in the Oxygen editor.
- If the attribute doesn't exist yet, you can select the Protected option when you create it.
- Follow the steps in: Create an attribute.


To protect an attribute:

 Update.
Update. Result: The
Result: The 
 After an attribute is created, you cannot change the
After an attribute is created, you cannot change the